J2EE
- About Servlet
- Deployment Descriptor
- Web Container
- Servlet Container
- Servlet API
- Life Cycle of Servlet
- Load On Start up
About Servlet
- Interfae b/w Appln Server, Web Server
- Receive Request and generates dynamic Response
Servlet Container
Part of web server interacts with servlet for handling for dynamic web pages from client
- Managing life cycle of servlet
- mapping incoming request to servlet [base on access)
- Servlet exceutes on web container which provides multithreaded environment
- so servlet can handle multiple request at same time
- we mostly use HttpServlet
Container States
- Standalone - Java Based server, servlet container and web server as single [Tomcat running itself)
- In-Process - Separate from web server [Tomcat running inside JBoss)
- Out-of Process -Web server uses plugin provided by the servlet container [both are different pgms)
Operations
- Security, Object Polling, Life cycle management of servlet, multithreaded support
Servlet API
- Two important packages javax.servlet and javax.servlet.https
- sevlet packges contains contains classes and Interfaces used by servlet and web container
- servlet.http responsible for http request only. nseWrapper, HttpServletRequestWrapper, HttpSessionEvent, HttpSessionBindingEvent
Deployment Descriptor
- web.xml file present in webapp –WEB-INF in maven project or webcontent-WEB-INF folder in the dynamic web project.
- servlet mapping defined here
- Sample web.xml here
More Detalis on Deployment Descriptor
Servlet Interfaces
Servlet interface provides common behaviour to all the servlets. Servlet interface needs to be implemented for creating any servlet [either directly or indirectly). It provides 3 life cycle methods that are used to initialize the servlet, to service the requests, and to destroy the servlet and 2 non-life cycle methods.
Refer Code Here SevletExample.java
Read code comment understand each of life cycle methods
Generic Servlet
- It implements Servlet, ServletConfig, Serializable interface, provides implementation of all methods of these interface except service method.
- It handles any type of request, so it is protocol-independent.
Refer code Here GenericServletExample.java
HTTP Servlet
The mostly used approach is by extending HttpServlet because it provides http request
- This class [HttpServlet) extends Generic Servlet
- It provides http specific methods like doGet, doPost, etc…
- Some interfaces are HttpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse, HttpSession, HttpSessionListener, HttpSessionAttributeListener, HttpSessionBindingListener, HttpSessionActivationListener
- Classes are HttpServlet, Cookie, HttpServletResponse
Ref: https://docs.oracle.com/javaee/7/api/javax/servlet/http/HttpServlet.html Example Code Here Hello.java
Life Cycle of Servlet
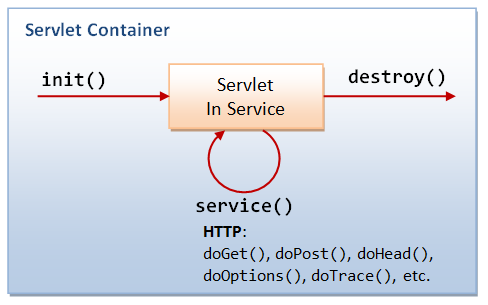
- Servlet Class Loaded
- class loader responsible for load servlet class [It load when first request received by web container)
- Servlet Instance created
- Web container create in of Servlet after Servlet class loaded, it happpened only once in life cycle
- init method invoked
- web container call init method after servlet instance created, it used to init the servlet, this method present in javax.servlet.Servlet interface
- service method called
- The web container calls the service method each time when request for the servlet is received.
- If servlet is not initialized, it follows the first three steps as described above then calls the service method.
- If servlet is initialized, it calls the service method. Notice that servlet is initialized only once.
- destroy method called
- web container calls the destroy method before removing the servlet instance from the service.
- used for clean up any resource for example memory, thread etc.
To hands on with servlet and how its working Read and to yourself Servlet Basics Hands-On